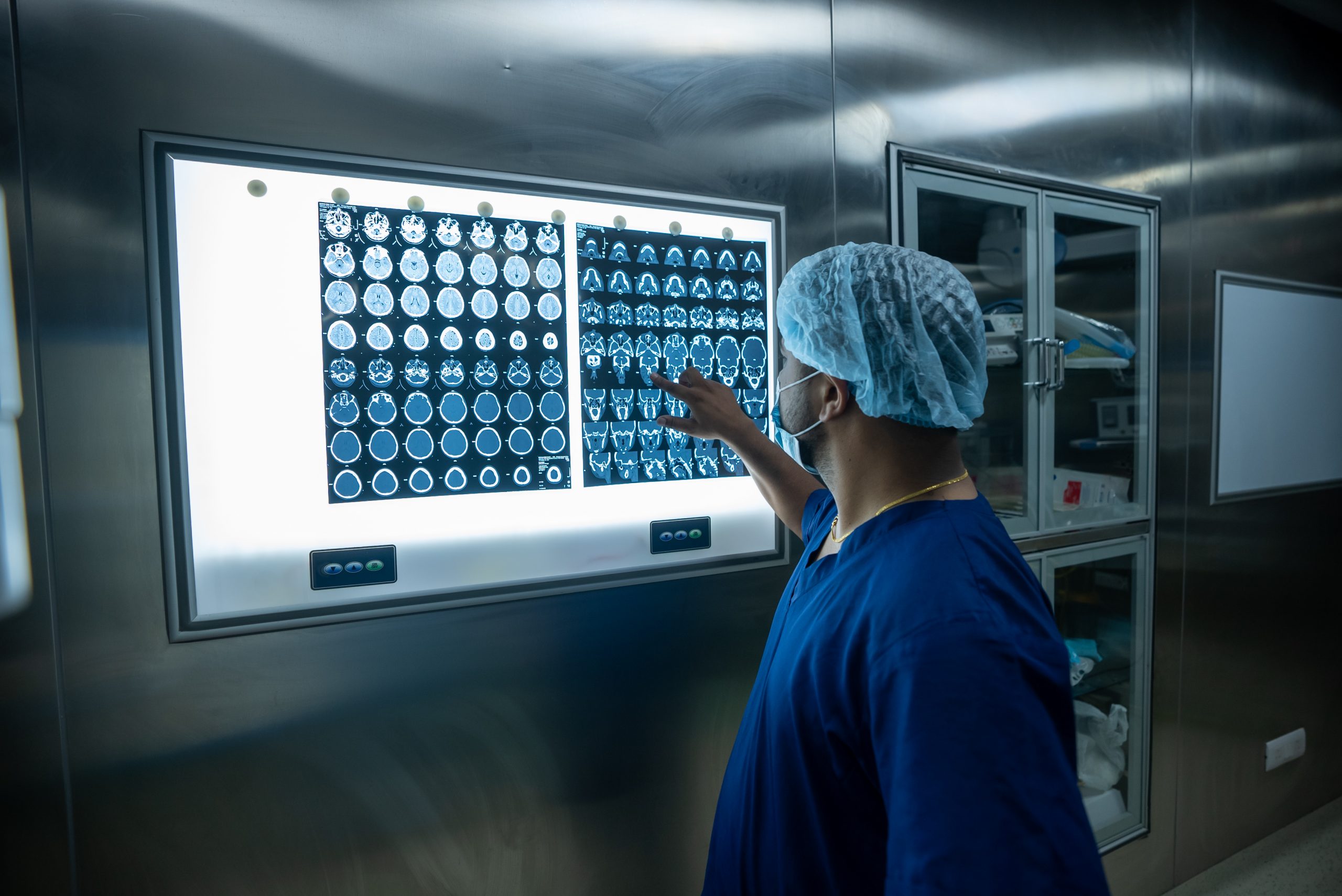
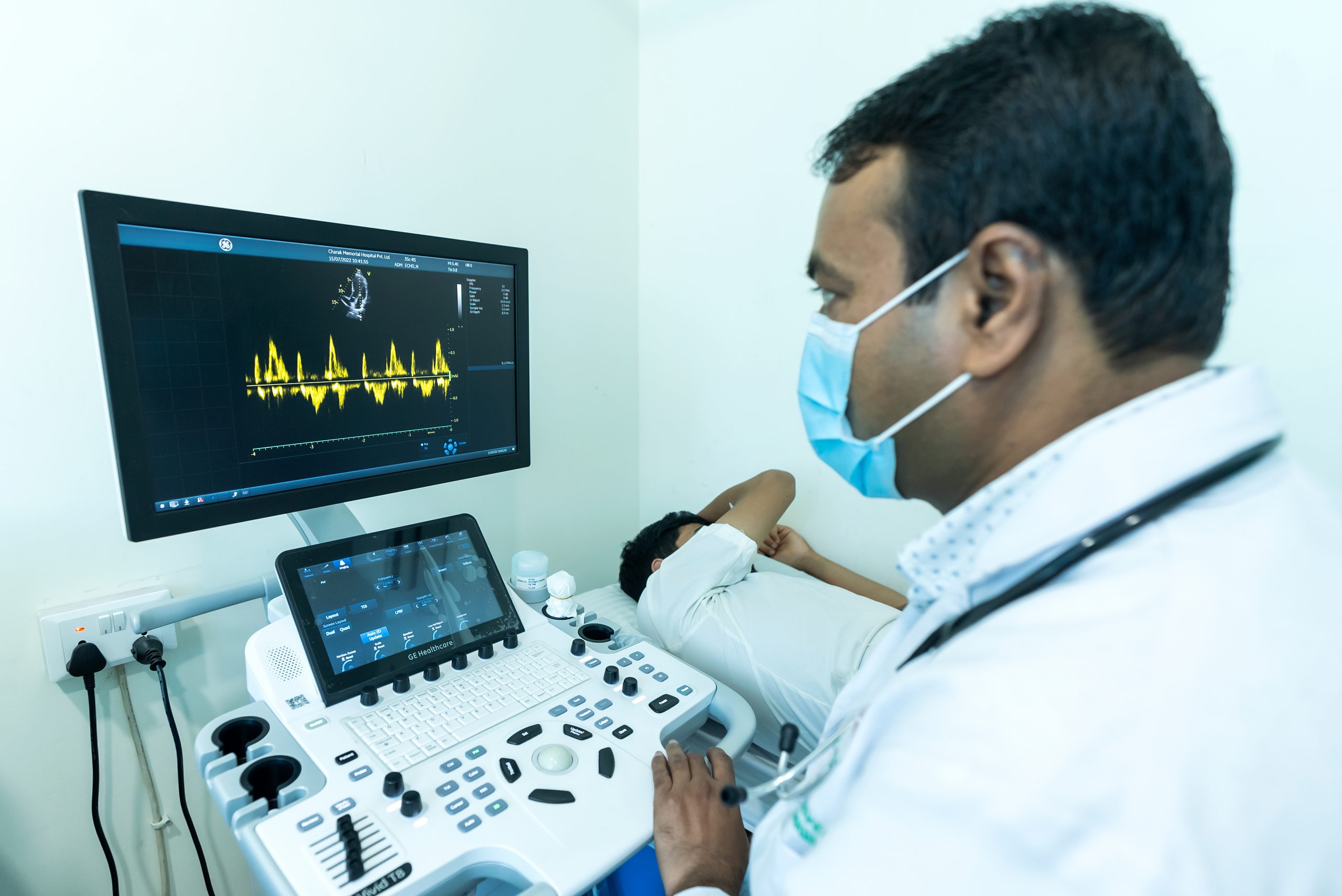
Radiology uses medical imaging technology to diagnose and treat diseases. Basically, radiology involves imaging the inside of the human body. It uses different imaging modalities like electromagnetic radiation, ultrasonography, magnetic resonance, fluoroscopy, nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography, etc to give the result.
There are following branches of radiology: